| [1]Hunter W. On the structure and diseases of articulating cartilage.Phil Trans 1743; 42B:514-521.
[2]Shapiro F, Koide S, Glimcher MJ. Cell origin and differentiation in the repair of full-thickness defects of articular cartilage. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75(4):532-553.
[3]Hunziker EB, Rosenberg LC. Repair of partial-thickness defects in articular cartilage: cell recruitment from the synovial membrane. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78(5):721-733.
[4]Piasecki DP, Spindler KP, Warren TA,et al. Intraarticular injuries associated with anterior cruciate ligament tear: findings at ligament reconstruction in high school and recreational athletes. An analysis of sex-based differences. Am J Sports Med. 2003;31(4):601-605.
[5]Curl WW, Krome J, Gordon ES,et al. Cartilage injuries: a review of 31,516 knee arthroscopies. Arthroscopy. 1997;13(4): 456-460.
[6]O'Driscoll SW, Keeley FW, Salter RB. Durability of regenerated articular cartilage produced by free autogenous periosteal grafts in major full-thickness defects in joint surfaces under the influence of continuous passive motion. A follow-up report at one year. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988; 70(4): 595-606.
[7]Salter RB, Simmonds DF, Malcolm BW,et al. The biological effect of continuous passive motion on the healing of full-thickness defects in articular cartilage. An experimental investigation in the rabbit.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980;62(8): 1232-1251.
[8]Mithöfer K, Peterson L, Mandelbaum BR,et al. Articular cartilage repair in soccer players with autologous chondrocyte transplantation: functional outcome and return to competition.Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(11):1639-1646.
[9]Behrens P, Ehlers EM, Köchermann KU,et al. New therapy procedure for localized cartilage defects. Encouraging results with autologous chondrocyte implantation. MMW Fortschr Med.1999;141(45):49-51.
[10]Matsusue Y, Yamamuro T, Hama H. Arthroscopic multiple osteochondral transplantation to the chondral defect in the knee associated with anterior cruciate ligament disruption. Arthroscopy. 1993;9(3):318-321.
[11]黄华扬,尹庆水,章莹,等.关节镜下带骨软骨镶嵌移植修复软骨病损[J].中华外科杂志,2002,40(9):662-665.
[12]智发朝,张兰军,彭秀凡,等.用生物型人工食管进行食管重建的实验研究[J].中华消化杂志,2003,23(3):137-141.
[13]史志东,陈明振,郭英,等.生物型硬脑膜原位植入转归的实验研究[J].中华神经精神疾病杂志,2005,31(4):260-263. |
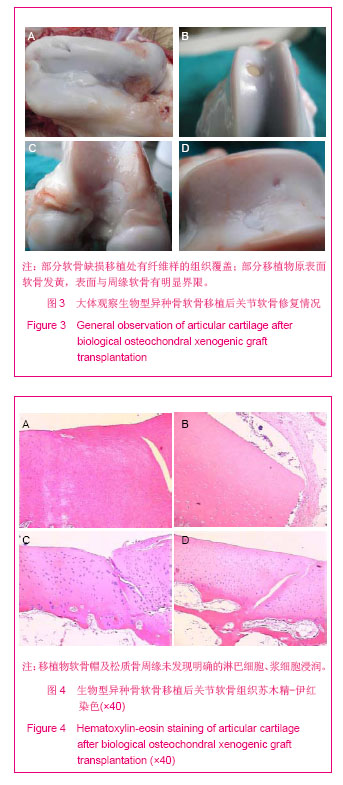
.jpg)
.jpg)